Hybrid Modulation
What is Modulation
Modulation is a
technique used to send information by modifying the characteristics of a basic
electromagnetic signal. The basic signal is called the carrier signal.
The characteristics
of a signal are amplitude, frequency and phase.
There are two
types of modulations as:
·
Analog Modulation
1. Frequency
Modulation (FM)
2. Amplitude
Modulation (AM)
3. Phase
Modulation (PM)
·
Digital Modulation
1. Frequency
Shift Keying (FSK)
2. Amplitude
Shift Keying (ASK)
3. Phase
Shift Keying (PSK)
What is Hybrid Modulation?
Hybrid
modulation is a combination of ASK and PSK. This method of modulation is called
Amplitude Phase Shift Keying (APSK) or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
It generates by quadrature components with two independent carrier signals with
same frequency and different amplitude which are transmitted simultaneously in
same medium and phase by shifting 90 degrees with respect to the other. This is
mainly used in as a modulation scheme for digital telecommunication signal and
in wireless standards. Some examples are microwave digital radio, DVB-C
(Digital Video Broadcasting – Cable) and modems.
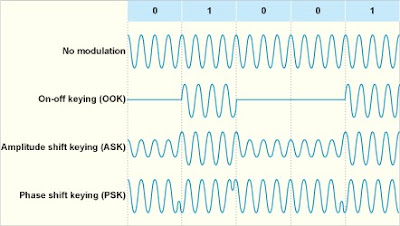
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
Amplitude
Shift Key is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as
variation in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, the binary
symbol 1 is represented by transmitting fixed amplitude carrier wave and fixed
frequency for a bit duration of t seconds.
Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
Phase
Shift Keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or
modulating, the phase of a reference signal (the carrier wave). Any digital
modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital
data.
Ø The
PSK has different versions,
·
BPSK (Bipolar Phase Shift Keying)
· QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying)
·
8PSK
·
16PSK
QAM is be being used in optical
fiber systems as bit rates increase; QAM16 and QAM64 can be optically emulated
with a 3-path.
Diagrams
of Hybrid Modulation
Encode a big bit stream:
001010100011101000011110
Break it up into 3-bit
triads:
001-010-100-011-101-000-011-110
Advantages and
Disadvantages of QAM
v Advantages
1. Allows
for more data to be transmitted over roughly the same bandwidth as simple AM.
2. It
increases the efficiency of transmission.
v Disadvantages
1. Lower
levels of noises needed to move the signal to a different decision point and
this noise can be problem with QAM.







Comments
Post a Comment